Word 2003 -
Edit Tables

Word 2003
Edit Tables


/en/word2003/working-with-tables/content/
Once you have created your table, you may find that you need to format text within your table, insert or delete rows and columns, or perhaps just change the appearance of your table so it is more visually appealing.
Formatting text in tables
Fortunately, whatever you do to format text in a paragraph (make it bold green, for example), you can do to text in a table cell. Formatting text within a table can be accomplished through a variety of means, including the Formatting menu, the Tables and Borders toolbar, the task pane, and keyboard shortcuts.
Rotating text in tables
Many advertisements, for-sale signs, menus, and other creative documents use Word's text direction feature to change typical horizontal text to eye-catching vertical text. You can rotate text so it runs vertically, facing either the right or the left.
 : on the Tables and Borders toolbar.
: on the Tables and Borders toolbar.
 The insertion point rotates when entering vertical text, but editing vertical text is no different from editing horizontal text.
The insertion point rotates when entering vertical text, but editing vertical text is no different from editing horizontal text.
Estimating how many rows and columns you will need in a table is not always easy. Therefore, it is important to know how to insert and delete rows and columns in your existing table.
 Insert
Insert  Rows above OR Rows below.
Rows above OR Rows below. Delete
Delete  Rows.
Rows.OR
 Delete
Delete  Rows from the shortcut menu.
Rows from the shortcut menu. Delete
Delete  Cells from the menu bar. The Delete Cells dialog box appears.
Cells from the menu bar. The Delete Cells dialog box appears.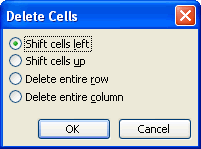
 Insert
Insert 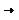 Insert Columns to the Right or Insert Columns to the Left.
Insert Columns to the Right or Insert Columns to the Left.
You may need to adjust the size of columns, rows, and cells.
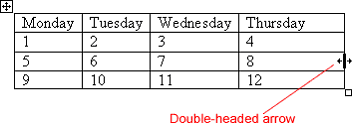
 To automatically adjust the size, select the entire table and then choose Table
To automatically adjust the size, select the entire table and then choose Table  AutoFit
AutoFit  AutoFit to Contents.
AutoFit to Contents.
AutoFormat
Just as Word offers document templates for memos, faxes, reports, and other items, it also offers templates for tables.
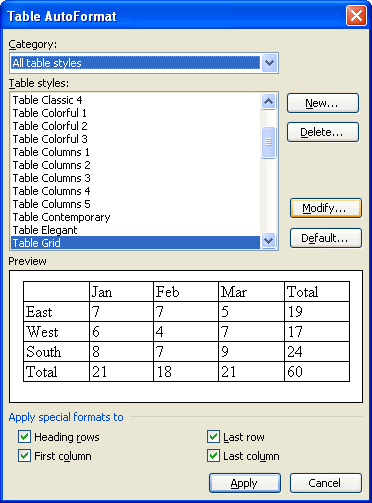
Many of the tables in the AutoFormat dialog box use unique borders and shading options. To add these special features to your own table, you can use the Tables and Borders toolbar.
You can access many of the features from the Table and Borders dialog box on the task pane. Choose the Reveal Formatting Menu and look for the Table and Cell Headings.
/en/word2003/working-with-objects/content/