Windows Basics -
All About Windows

Windows Basics
All About Windows


Windows is an operating system designed by Microsoft. The operating system is what allows you to use a computer. Windows comes preloaded on most new personal computers (PCs), which helps to make it the most popular operating system in the world.
Windows makes it possible to complete all types of everyday tasks on your computer. For example, you can use Windows to browse the Internet, check your email, edit digital photos, listen to music, play games, and do much more.
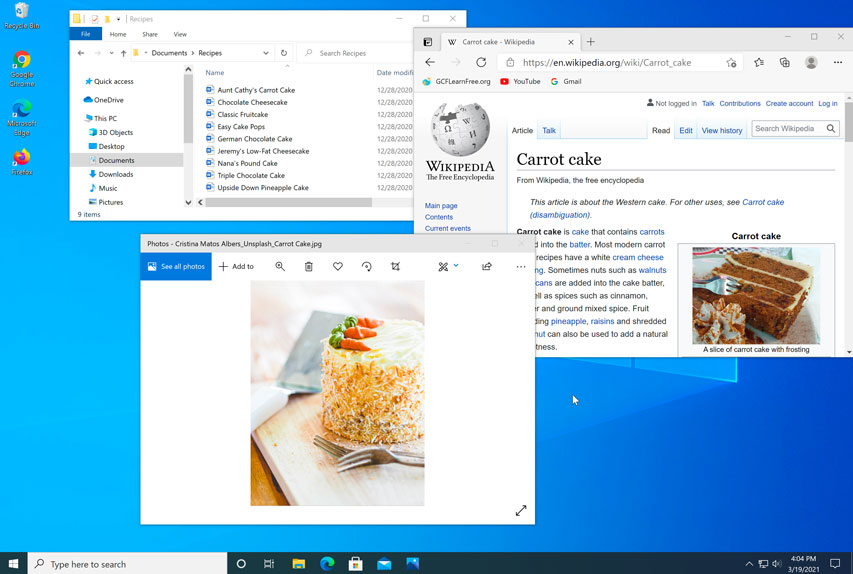
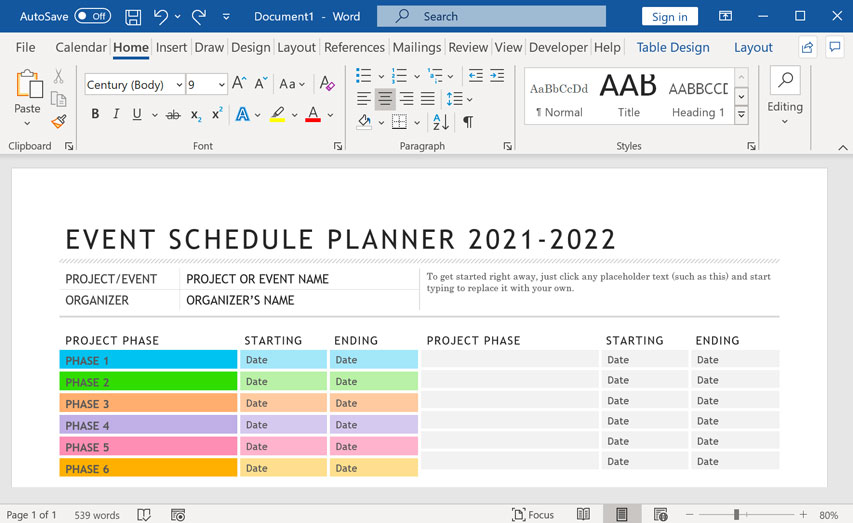
Windows is also used in many offices because it gives you access to productivity tools such as calendars, word processors, and spreadsheets.
Microsoft released the first version of Windows in the mid-1980s. There have been many versions of Windows since then, but the most recent ones include Windows 10 (released in 2015), Windows 8 (2012), Windows 7 (2009), Windows Vista (2007), and Windows XP (2001).
This tutorial is designed to show you the absolute basics of using a Windows computer, including how to use the desktop, how to open different files and applications, and how to move and resize windows. The information in this tutorial will apply to more recent versions of Windows, including the ones mentioned above. However, once you've learned the basics, you may also want to review one of our version-specific Windows tutorials. Just select the version of Windows that's installed on your computer:
While most versions of Windows are relatively similar, Windows 8 works very differently from other versions. However, if you have Windows 8 on your computer, you should now be able to upgrade to Windows 10, which is more similar to earlier versions, including Windows 7. We recommend upgrading your computer to Windows 10 if you can. Review our Windows 10 tutorial to learn how.
However, we'll still point out any major differences between Windows 8 and other versions, which means you'll see some Windows 8-specific information from time to time. If your computer uses Windows 8, you'll want to review both this tutorial and our Windows 8 tutorial to learn more about the differences.
/en/windowsbasics/navigating-windows/content/