Windows 98 -
The Desktop

Windows 98
The Desktop


Windows 98 is an operating system that lets you use different types of applications or software. For example, it allows you to use a word processing application to write a letter and a spreadsheet application to track your financial information.
This operating system has multi-tasking capabilities, meaning it can run several applications at the same time. Multi-tasking allows you to view this lesson on the Internet at the same time you practice using other applications with Windows 98.
The opening screen of Windows 98 is called the desktop. This workspace on your computer screen contains:
The Start button,  in the lower-left corner of your desktop, is one of the most important tools you will use while working with Windows 98. The Start button allows you to open menus and start applications.
in the lower-left corner of your desktop, is one of the most important tools you will use while working with Windows 98. The Start button allows you to open menus and start applications.
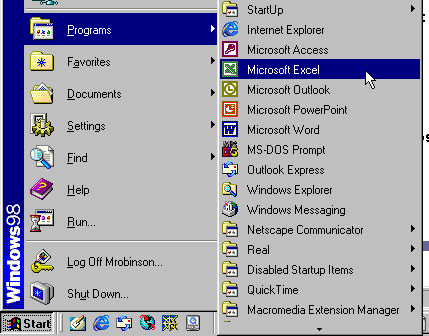
When you click the Start button, a pop-up menu (the Start menu) appears. The Start menu shows all of the applications that are on your computer. It also lists several options, including Shutdown, Help, Find, and Programs.
If you select Programs, a pop-up menu appears. Pop-up menus like this are called cascading menus. If a cascading menu is available, a small black triangle appears next to the name of the application or function.
In the example below, the Microsoft Excel program has been selected.
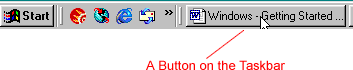
When you turn on the computer, the taskbar appears as an empty gray area at the bottom of the screen. When a window or application is open on the desktop, you can see a rectangular button on the taskbar that shows the name of the application.
The small pictures on the desktop are called icons. One type of icon is an object icon. Examples of object icons are My Computer, Recycle Bin, and Internet Explorer. These icons allow you to open applications and documents on your computer.
![]()
A shortcut icon has a small jump arrow in the left corner. You can use a shortcut icon to open an application quickly. The icon below is a shortcut icon for the Microsoft Word application found on the Start menu. You don't have to use the Start menu to access the application if you have a shortcut for it on your desktop. You'll learn about creating shortcuts in a later lesson.
![]()
Remember, you should never just turn off the computer. To avoid damage to the system or loss of files, always follow specific steps to shut down the computer. The Start menu is where you begin the shutdown process.
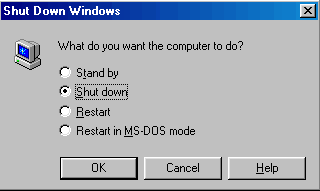
 The message "Windows 98 is shutting down" appears. When the computer screen goes dark, Windows 98 has shut down. You can choose to leave your monitor on or turn it off.
The message "Windows 98 is shutting down" appears. When the computer screen goes dark, Windows 98 has shut down. You can choose to leave your monitor on or turn it off.
Dialog boxes feature button, boxes, tabs, and sliders to help you control how your computer looks and works. You should become familiar with the various dialog box controls.
 Command button
Command button
![]()
This tells the computer to carry out an action. Click on this button to execute a command.
 Option button
Option button

This button, which looks like a circle, appears when you have a list of choices. Click inside the circle to select only one option.
 Check boxes
Check boxes
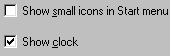
These appear when a list of options is available. Click inside the boxes to select one or more options.
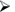 Text box
Text box

This provides space for you to type information. For example, when you name a file you type in a text box.
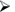 Spin box
Spin box

This sets a value, such as the number of copies to print. A spin box is a text box next to an up arrow and a down arrow. The text box contains a number. Click the up or down arrow to increase or decrease the number.
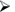 List box
List box

This is a white space that contains a list of options. Click on an option to select it.
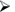 Drop-down list box
Drop-down list box
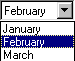
This shows only one option at a time (the option that is selected), and there is an arrow at the end of the box. Click the arrow to see the entire list of options.
 Tabs
Tabs
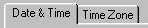
These resemble file folder tabs. When you click on a tab, a page of information appears.
 Slider
Slider
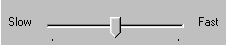
This looks like a sliding volume control on a radio. It lets you set a value within a range of values, such as from slow to fast. To move a slider, place the mouse pointer on the slider, hold down the left mouse button, and drag it.
/en/windows98/programs-and-favorites/content/