Email Basics -
Common Email Features

Email Basics
Common Email Features


/en/email101/introduction-to-email/content/
No matter which email service you choose, you'll need to learn how to interact with an email interface, including the inbox, the Message pane, and the Compose pane. Depending on the email provider, the interfaces may look and feel different, but they all function in essentially the same way.
In this lesson, we'll talk about using an email interface to send and receive messages. We'll also discuss various terms, actions, and features that are commonly used when working with email.
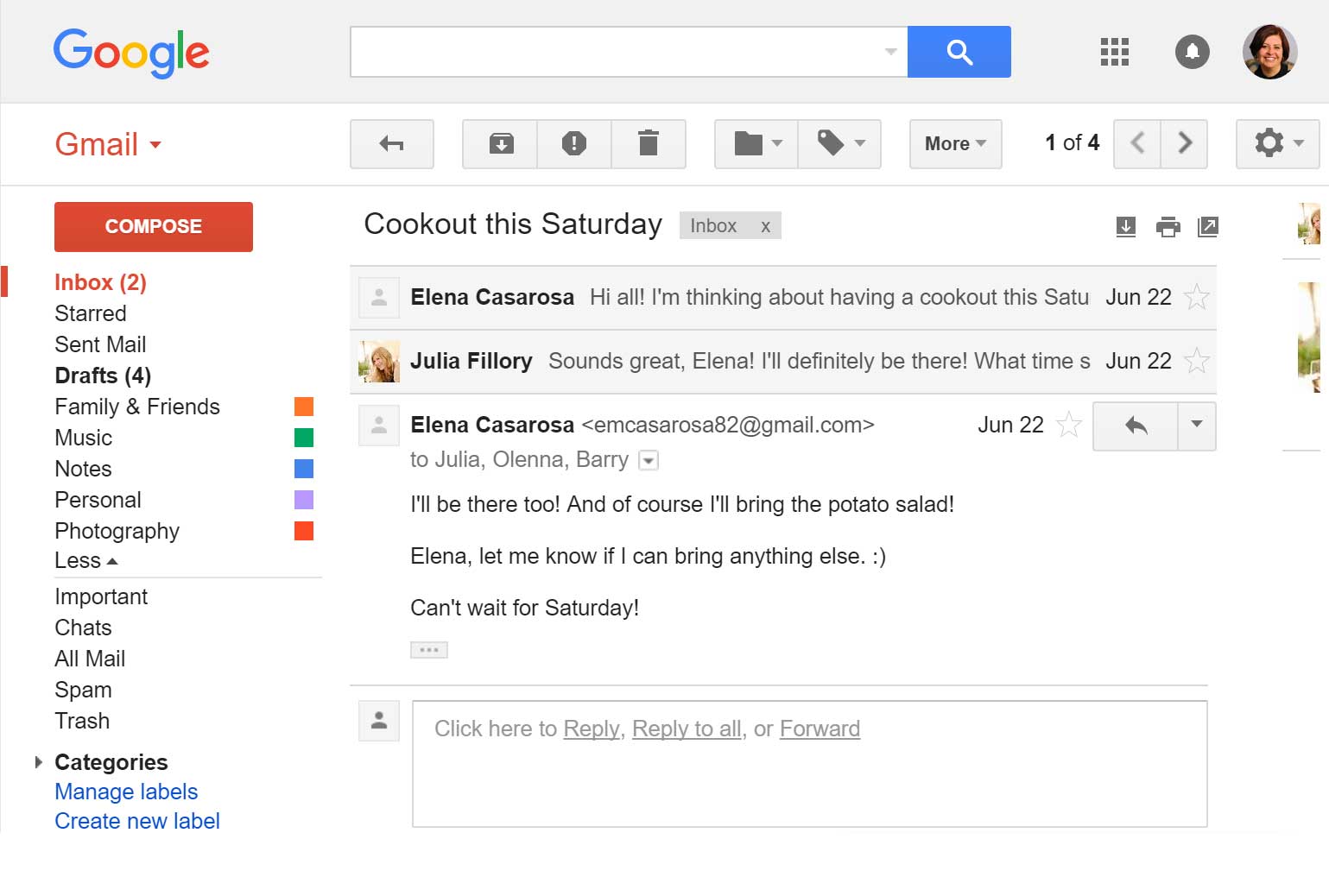
Below are some examples of different email interfaces from Gmail. Review the images below to become familiar with various email interfaces.
Keep in mind that these examples will only provide a general overview. You can visit our Gmail tutorial to learn how to use an email application in detail.
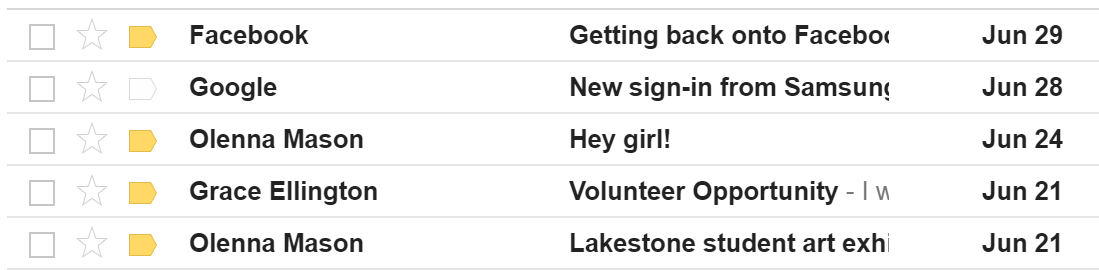
The inbox is where you'll view and manage emails you receive. Emails are listed with the name of the sender, the subject of the message, and the date received.
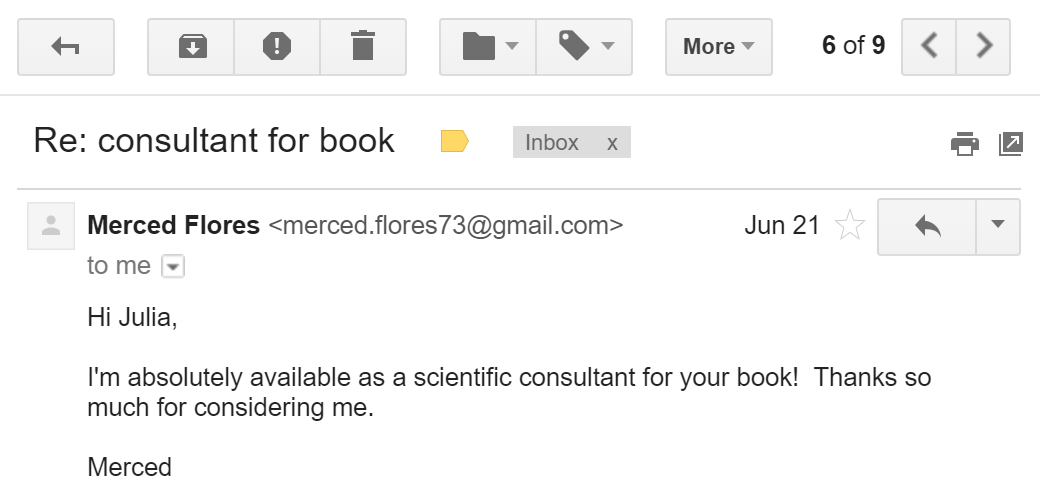
When you select an email in the inbox, it will open in the Message pane. From here, you can read the message and choose how to respond with a variety of commands.
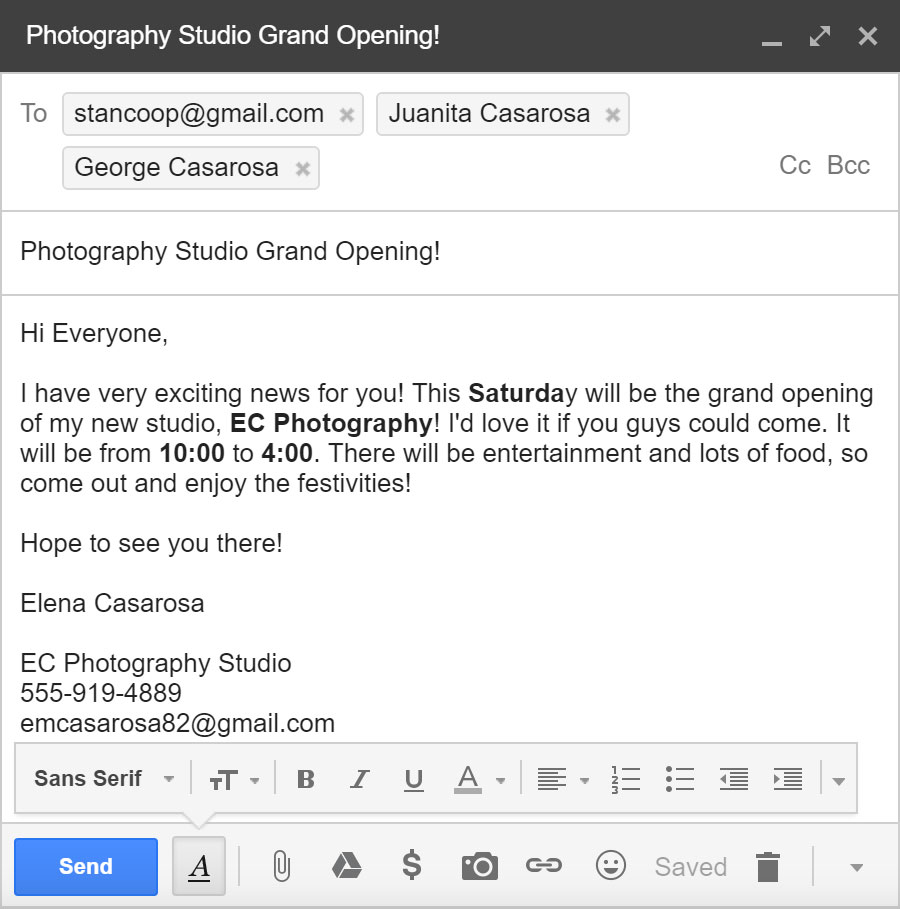
You can click the Compose or New button from your inbox to open the Compose pane to create your own email message. From here, you'll need to enter the recipient's email address and a subject. You'll also have the option to upload files (photos, documents, etc.) as attachments and add formatting to the message.
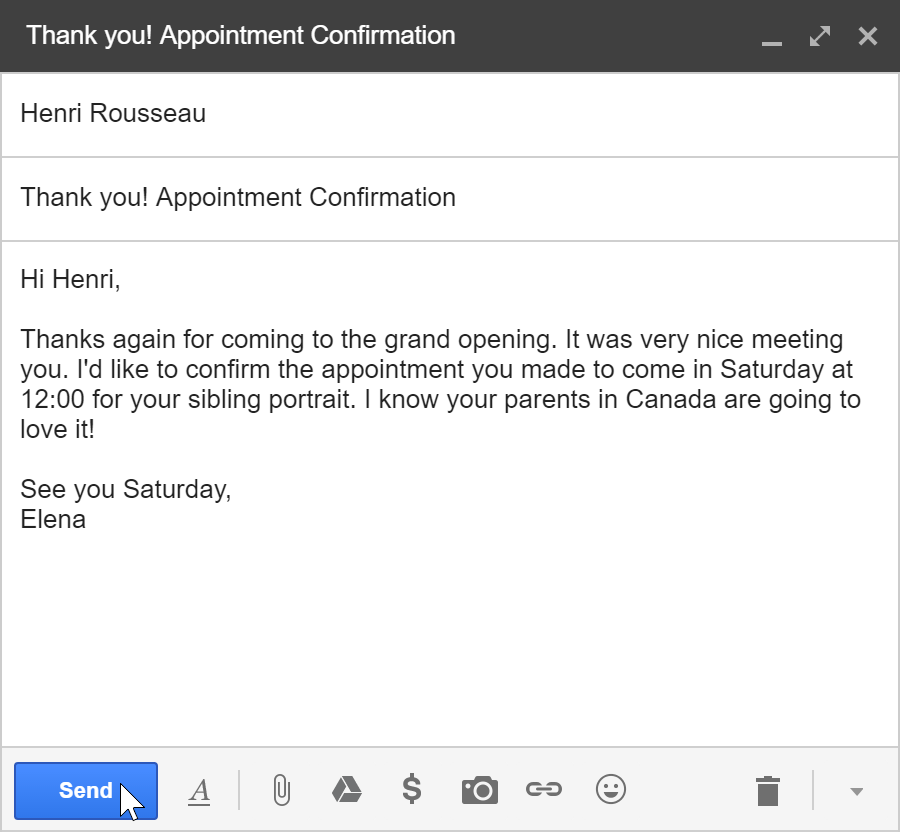
A Compose pane will also appear when you select Reply or Forward. The text from the original message will be copied into the Compose pane.
All email applications use certain terms and commands you will need to understand before using email. The examples below use Gmail's Compose pane and Message pane to introduce basic email terms, but these will still be applicable for Yahoo! and Outlook.
Click the buttons in the interactive below to learn more about the Compose pane.
Click the buttons in the interactive below to learn more about the Message pane.
/en/email101/contacts-and-calendars/content/